NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Science Chapter 1 Crop Production and Management provides solutions to all questions given in NCERT Textbook. Our expertly crafted solutions provide detailed, step-by-step answers to all textbook questions, making it easier for students to grasp complex concepts. By using our solutions, students can enhance their understanding, improve their problem-solving skills, and boost their confidence in the subject.
| Chapter | Crop Production and Management |
| Textbook | NCERT |
| Type of Material | NCERT Solutions |
| Class | 8 |
| Subject | Science |
| Useful for | Class 8 Studying Students |
| Session | 2024-25 |
| Solutions provided | Yes |
| Intext Questions | Solved |
| No. of Intext Questions | 9 |
| No. of Exercise Questions | 11 |
| Total Questions Solved | 20 |
| Important Link | NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Science |
Class 8 Science Chapter 1 Crop Production and Management NCERT Solutions
INTEXT QUESTIONS SOLUTIONS
Page – 1
Q. 1. Boojho wants to know where we use the tools like khurpi, sickle, shovel, plough, etc.?
Ans. We use tools like khurpi, sickle, shovel, plough, etc., in agricultural activities.
Q. 2. Boojho wants to know, since we all need food, how can we provide food to a large number of people in our country?
Ans. Food will have to be produced on a large scale. In order to provide food for a large population, regular production, proper management and distribution of food are necessary.
Q. 3. Boojho wants to know why paddy cannot be grown in the winter season.
Ans. Paddy requires a lot of water. So, it is grown only in the rainy season.
Page -4
Q. 4. One day Paheli saw her mother put some gram seeds in a vessel and pour some water on them. After a few minutes, some seeds started to float on the top.
She wondered why some seeds floated on water?
Ans. Damaged seeds become hollow and are thus lighter. Therefore, they floation water.
Page -5
Q. 5. Boojho saw one nursery near his school. He found that little plants were kept in small bags. He wants to
know, why?
Ans. Seeds of a few plants such as paddy are first grown in nursery. When small plantlets are formed, they are transplanted in the field manually. Some forest plants and flowering plants are also grown in the nursery.
Q. 6. Boojho went to a farm and saw a healthy crop growing there. Whereas in the neighbouring farm the plants were weak. He asked Paheli why do some plants grow better than others?
Ans. This is because of insufficient manuring and care.
Page-10
Q. 7. Boojho told the farmer that there were other plants growing along with wheat. He wanted to know if they had been purposely grown.
Ans. No, in a crop field many other undesirable plants may grow naturally along with the crop, these are called weeds.
Q. 8. Boojho wants to know whether weedicides have any effect on the person handling the weedicide sprayer. Ans. Yes, sprayer of weedicide may affect the health of farmers.
Page-11
Q. 9. One day Paheli saw her mother putting some dried neem leaves in an iron drum containing wheat. She wondered, why?
Ans. This prevents the attack by insects, pests, bacteria and fungi.
EXERCISE QUESTIONS SOLUTIONS
Q. 1. Select the correct word from the following list and fill in the blanks:
float, water, crop, nutrients, preparation.
(i) The same kind of plants grown and cultivated on a large scale at a place is called _________.
(ii) The first step before growing crops is _________ of the soil.
(iii) Damaged seeds would _________ on top of water.
(iv) For growing a crop, sufficient sunlight, _________ and _________ from the soil are essential.
Ans. (i) crop, (ii) preparation, (iii) float, (iv) water, nutrients
Q. 2. Match the items in column I with those in column II.
| Column I | Column II |
| (i) Kharif crops | (a) Food for cattle |
| (ii) Rabi crops | (b) Urea and superphosphate |
| (iii) Chemical fertilisers | (c) Animal excreta, cow dung urine and plant wastes |
| (iv) Organic manure | (d) Wheat, gram, pea |
| (e) Paddy and maize |
[NCERT Ex. Q.2. Page 14]
Ans. (i) (e), (ii) (d), (iii) (b), (iv) (c)
Q. 3. Give two examples of each: (i) Kharif Crop (ii) Rabi crop
[NCERT Ex. Q.3. Page 14]
Ans.
(i) Kharif Crop: Soyabean and Groundnut.
(ii) Rabi Crop: Pea and mustard.
Q. 4. Write a paragraph in your own words on each of the following:
(i) Preparation of soil (ii) Sowing (iii) Weeding (iv) Threshing.
[NCERT Ex. Q.4. Page 14]
Ans. (i) Preparation of soil: Soil is prepared before sowing the seeds. The soil is loosened to increase the absorption of water and manure. Loosening of soil particles adds humus and nutrients in the soil that increases crop yields. Tilling or loosening the soil is done by plough which is pulled by a pair of bulls. Tractor driven cultivators are also used to loosen the soil.
(ii) Sowing: After preparation of soil, it is ready for sowing of seeds. Healthy and clean seeds should be selected. Sowing is done by seed drill or funnel shaped tools. Seed drill is a modern instrument which can sow seeds at proper depth and distance.
(iii) Weeding: The unwanted plants that grow along with the crops are called weeds. They hinder the growth of plant, by absorbing nutrients from the soil. Thus, it is necessary to remove them, otherwise, they make the soil nutrient deficient. The process of removing weeds is called weeding. It can be done manually or by mechanical tools. Some chemicals like 2,4-D can also be used.
(iv) Threshing: The separation of grains from the chaff is called threshing. When the crop matures, it is harvested and cut along with the stalks. Grains are then separated from the chaff using a winnowing machine.
Q. 5. Explain how fertilisers are different from manures.
[NCERT Ex. Q.5. Page 14]
Ans. (i) Manures are organic substances, while fertilisers are chemical substances.
(ii) Manures are prepared in fields, while fertilisers are prepared in factories.
(iii) Manures contain all the nutrients, while fertilisers are rich in certain nutrients.
(iv) Manures provide humus, while fertilisers do not.
Q. 6. What is irrigation? Describe two methods of irrigation which conserve water.
[NCERT Ex. Q.6. Page 14]
Ans. The supply of water to crops at different intervals is called irrigation. Latest irrigation methods help us to use water economically.
The main methods used are as follows:
(i) Sprinkler system: This system is more useful on the uneven lands where water is available in smaller quantity. The perpendicular pipes, having rotating nozzles on the top, are joined to the main pipe lines at regular intervals. When the water is allowed to flow through the main pipe with the help of a pump, it escapes from the rotating nozzles. It is sprinkled on the crop as if it is raining. A sprinkler is very useful for sandy soil.
(ii) Drip system: In this system, the water falls drop by drop just at the position of the roots. So, it is called drip system. It is the best technique of watering fruit plants, gardens and trees. This system consists of a main pipe to which lateral pipes are joined. The specially prepared nozzles are attached to these lateral pipes. The nozzles are grounded just near the roots of the plants. Water is not wasted at all. So, it is a boon in regions where the availability of water is poor.
Q. 7. If wheat is sown in the Kharif season, what would happen? Discuss.
[NCERT Ex. Q.7. Page 14]
Ans. Wheat’s seeds need low temperature and less humidity to grow. If they are sown in Kharif season (i.e., rainy season), the seeds would get destroyed due to excess of water and would not grow.
Q. 8. Explain how soil gets affected by the continuous plantation of crops in a field.
[NCERT Ex. Q.8. Page 14]
Ans. Soil is the source for plants from which they derive their mineral nutrients, essential for their growth. If crops are grown continuously in the same field, for a long period of time, the soil becomes deficient in nutrients. Thus, the field becomes infertile.
Q. 9. What are weeds? How can we control them?
[NCERT Ex. Q.9. Page 14]
Ans. Weeds are the undesirable (unwanted) plants that may grow naturally along with the crops. They are hazardous to the crops as they compete with the crop for food, nutrients, water and sunlight. Hence, they must be controlled. The process of controlling or removing weeds from the field is known as weeding. There are several methods to remove weeds such as tilling in which weeds are uprooted. They are also controlled by chemicals known as weedicides which kill the weeds, e.g., 2,4 -D.
Q. 10. Arrange the following boxes in proper order to make a flow chart of sugarcane crop production.
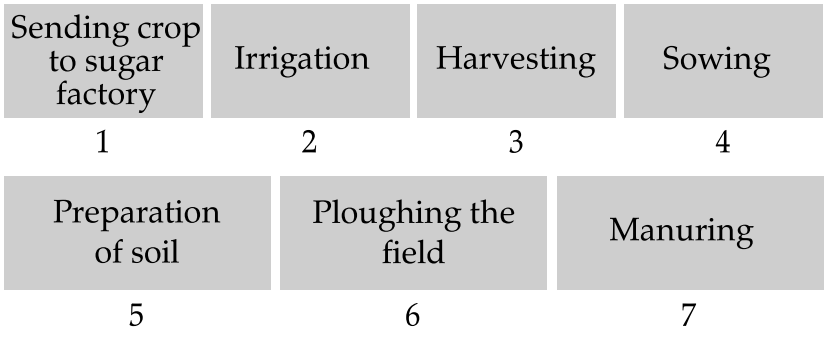
[NCERT Ex. Q.10. Page 14]
Ans.
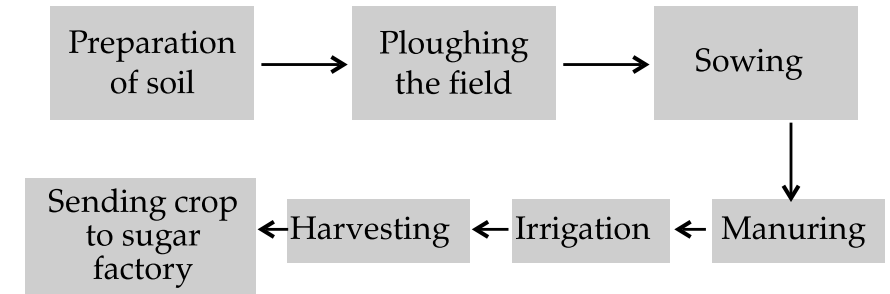
Q. 11. Complete the following word puzzle with the help of clues given below:
Down:
(1) Providing water to the crops.
(2) Crop grains have to be kept for a long time in proper conditions.
(5) Certain plants of the same kind grown on a large scale.
Across:
(3) A machine used for cutting the matured crops.
(4) A rabi crop that is also one of the pulses.
(6) A process of separating the grains from chaff.
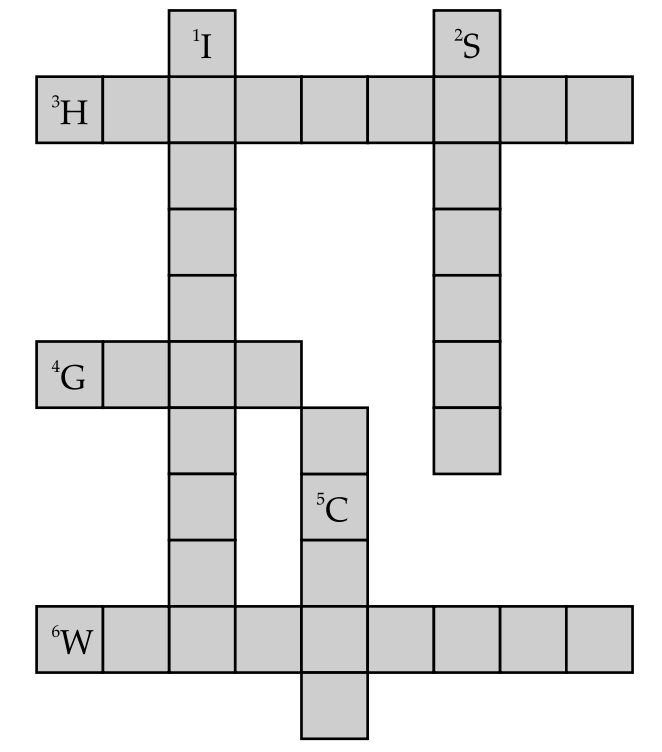
[NCERT Ex. Q.11. Page 15]
Ans. (1) Irrigation (2) Storage (3) Harvester (4) Gram (5) Crop (6) Winnowing
Learning Outcomes
Chapter 1 of Class 8 Science, “Crop Production and Management,” introduces students to the fundamental concepts of agriculture, crop production, and various agricultural practices. By the end of this chapter, students will have a clear understanding of how crops are grown, managed, and harvested.
- Knowing types of crops.
- Knowing how to protect crops from pests.
- Learning various agricultural practices involved in crop
- Discussing harvesting of crops and storage of grains. production.
- Discussing the irrigation methods used in agriculture.
- Knowing about animal husbandry.
By the end of Chapter 1, students will have a comprehensive understanding of the essential practices involved in crop production and management. They will be equipped with knowledge about the various techniques and methods used in agriculture, which are vital for producing food and sustaining life. This foundational understanding will prepare them for more advanced topics in agriculture and related sciences.
Also access
- NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Science Chapter 2 Microorganisms: Friend and Foe
- NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Science Chapter 1 Crop Production and Management
You may also like
- NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Maths
- NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Social Science
Topics covered in NCERT Class 8 Science Chapter 1
| 1.1 | Agricultural Practices |
| 1.2 | Basic Principle of Crop Production |
| 1.3 | Preparation of Soil |
| 1.4 | Sowing |
By referring to NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Science Chapter 1, students can quickly clarify difficult concepts. These solutions also ensure that students learn the correct answers to the exercise questions in their Class 8 Science NCERT textbook.
Stay connected to discover more about NCERT Solutions and get valuable preparation tips.
Important Links for Crop Production and Management
- Case Study Questions for Crop Production and Management Class 8 Science Chapter 1
- Assertion Reason Questions for Crop Production and Management Class 8 Science Chapter 1
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) on Crop Production and Management NCERT Solutions
Q1: What are NCERT Solutions?
A1: NCERT Solutions are detailed, step-by-step answers to the questions provided in the NCERT textbooks. They are designed to help students understand the concepts thoroughly and prepare effectively for their exams.
Q2: Why are NCERT Solutions important for students?
A2: NCERT Solutions are crucial for students because they offer clear explanations and step-by-step guidance on solving textbook problems. They help in building a strong foundation in each subject, making it easier for students to grasp complex concepts and perform well in their exams.
Q3: Are the NCERT Solutions available for free on NCERT Solved?
A3: Yes, all the NCERT Solutions on our website are available for free. We believe in making education accessible to all students, ensuring that everyone can benefit from our resources without any cost.
Q4: How can NCERT Solutions help in exam preparation?
A4: NCERT Solutions help in exam preparation by providing thorough explanations and solutions to textbook problems. They ensure that students understand the core concepts and are well-prepared for any type of question that may appear in their exams.
Q5: Are NCERT solutions enough for scoring good marks in Class 8 Science exams?
A5: Yes, NCERT solutions cover the entire syllabus prescribed by CBSE for Class 8 Science. If students thoroughly understand and practice these solutions, they can definitely score well in their exams. However, it’s also beneficial to supplement your studies with additional reference materials and practice questions.
Q6: Do you provide solutions for NCERT Exemplar problems as well?
A6: Yes, we provide comprehensive solutions for NCERT Exemplar problems for Classes 6 to 12. These exemplar solutions offer advanced practice problems that enhance critical thinking and problem-solving skills.
Q7: How often are the solutions updated on NCERT Solved?
A7: We regularly update our solutions to ensure they align with the latest NCERT curriculum.
Q8: Can parents and teachers use NCERT Solved Website for helping students?
A8: Absolutely! Our detailed solutions are beneficial not only for students but also for parents and teachers who are helping students in their academic journey. They can use our resources to better explain concepts and provide additional practice.
Q9: How can I access NCERT Solutions on NCERT Solved?
A9: Accessing NCERT Solutions on our website is simple. Just visit ncertsolved.com, select your class and subject, and you will find detailed solutions for each chapter and exercise.
Q10: What makes NCERT Solved different from other educational websites?
A10: NCERT Solved stands out due to our commitment to providing high-quality, meticulously crafted solutions for free. Our solutions are designed by experienced educators and subject matter experts, ensuring accuracy and clarity. We also regularly update our content to keep it aligned with the latest curriculum and exam patterns.
Q11: What are the important keywords in class 8 science chapter 1 “Crop Production and Management”?
A11: Important keywords from class 8 science chapter 1 crop production and management are given below:
Agriculture: Applied branch of biology which involves the practice of cultivating crops as well as rearing animals.
Cultivation of Soil: Digging soil to prepare it for planting.
Sowing: Process of scattering or putting seeds into the soil to grow a new crop plant.
Crop rotation: Practice of growing a series of different types of crops in the same field.
Silos: A tall tower on farm used to store grain.
Granaries: Storehouses for threshed grain.
Animal rearing: Process of raising, feeding and taking care of domestic animals.
Q12: What are some fundamental facts from Class 8 Science Chapter 1 Crop Production and Management?
A12: Fundamental facts –
(i) Till 10,000 B.C.E. people were nomadic and wandered in groups from place to place in search of food and shelter. They ate raw fruits and vegetables and hunted animals for food. Later, they started cultivating land and produce rice, wheat and other food crops thereby giving birth to ‘Agriculture’.
(ii) India is the second largest food producer in the World.
